Understanding Diabetes and How Dietary Choices Can Help Manage This Chronic Condition.
Diabetes is a serious and long-term condition that affects millions of people all around the world. Managing diet with diabetes is a lifelong commitment that requires a multilayer approach, including medication, regular exercise, and most importantly, a well-planned diet. The two most common types are Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes, which directly impact how the body regulates blood sugar.
This article will explore: what are some promising ways to manage diet with diabetes? by addressing key questions about the causes, symptoms, and types of diabetes, and how specific dietary strategies can help manage this condition effectively.
Importance of Diet in Managing Diabetes

Diet plays an important role in managing diabetes because it directly affects blood sugar levels, which are central to the condition. The following are the reasons to manage diet with diabetes:
Blood Sugar Management:
To manage diet with diabetes, our main focus is keeping blood sugar levels normal. The types and amounts of food consumed directly affect blood glucose levels. A well-balanced diet helps normalize these levels by providing a good energy source and preventing sharp spikes or drops in blood sugar.
Weight Direction:
Maintaining a fit weight is important for people with Type 2 diabetes. Extra weight can directly affect insulin resistance, making it more challenging for the body to control blood sugar. A diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and vegetables can support weight management and reduce the risk of any complications.
Nutrient Intake:
Diabetes management isn’t just about controlling blood sugar; it also includes the normal intake of essential nutrients. A balanced diet of various foods helps provide important vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and avoid diabetes-related difficulties.
Preventing Complications:
Consistent dietary habits can help manage diabetes-related problems such as heart disease, kidney damage, and neuropathy. Foods high in fiber, healthy fats, and antioxidants can improve cardiovascular health and support the function of organs and tissues affected by diabetes.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity:
Many foods can improve the body’s response to insulin, which makes it easier to normal blood sugar levels. Foods high in fiber and low in refined sugars can enhance insulin sensitivity, particularly beneficial for those with Type 2 diabetes.
Stabilizing Energy Levels:
Eating balanced meals and snacks throughout the day helps maintain normal energy levels and prevent fatigue. By managing carbohydrate intake and focusing on nutrient-dense foods, people with diabetes can avoid the energy crashes that can occur with bad food choices and easily manage their diet with diabetes.
Enhancing Quality of Life:
A well-planned diet can improve the overall quality of life for people with diabetes. It can help manage symptoms, reduce the risk of danger, and enhance emotional well-being by supporting a healthier, more balanced lifestyle.
Also, a thoughtful and well-structured diet with diabetes can help control blood sugar levels, support weight management, ensure normal nutrient intake, avoid complications, and improve overall well-being. Working with a healthcare provider or a dietitian to create a personalized dietary plan is important for good results.
What Are the Causes of Diabetes?
Understanding the causes of diabetes is important for better management and prevention. A combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors can take part in the development of diabetes.
– Genetic Aspects:
Genetics are significant in developing Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes. If you have a family history of diabetes, your risk of developing the condition is higher.
– Lifestyle and Environmental Factors:
Type 2 diabetes is strongly linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor diet, and lack of physical activity. A lifestyle combined with a diet high in processed foods and sugars can lead to insulin resistance, a main factor in Type 2 diabetes.
– Autoimmune Responses:
Type 1 diabetes is when the immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood, but it involves genetic and environmental factors.
What Are the Symptoms of Diabetes?
identifying the symptoms of diabetes early can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, which is very important for managing the disease and avoiding complications.
– Common Symptoms:
Some of the most common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and blurred vision. The symptoms mentioned earlier are mainly caused by high blood sugar levels, which can seriously damage different organs and systems in the body.
– Differences Between Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms:
While both types of diabetes share some common symptoms, there are differences. Type 1 diabetes symptoms tend to develop suddenly and are more severe, while Type 2 diabetes symptoms may develop gradually and be milder initially. This can make Type 2 diabetes harder to detect without regular screening.
What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
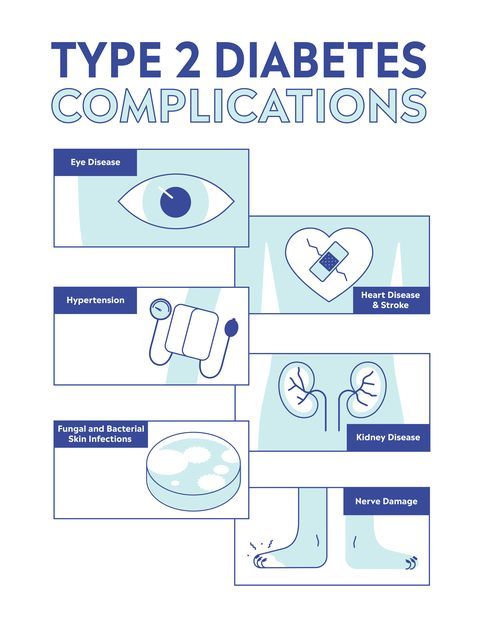
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for about 90% of all cases. It mainly happens when the body becomes immune to insulin or the pancreas stops producing enough insulin.
– Definition and Characteristics:
High blood sugar levels characterize type 2 diabetes due to insulin resistance and lack of insulin production. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, which usually develops in childhood or puberty, Type 2 diabetes commonly occurs in adults, although it is frequently diagnosed in young people.
– Risk Factors:
Risk factors for Type 2 diabetes include weight gain, lack of physical activity, poor diet, age, and a family history of the disease. A few ethnic groups, like African Americans, Hispanics, and Native Americans, are at higher risk.
– Control Via Diet and Lifestyle Changes:
Diet plays a powerful part in controlling Type 2 diabetes. A type 2 diabetes diet plan concentrates on maintaining blood sugar levels by preferring foods low in carbohydrates and sugars, rich in fiber, and high in vitamins and minerals. Workout has a strong role in adequate insulin sensitivity and healthiness.
What Is Type 1 Diabetes?

Type 1 diabetes is not a very common form of diabetes. It occurs when the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas and eradicates them.
– Definition and Characteristics:
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease that normally develops in childhood or teens but can develop at any age. Type 1 diabetes is not associated with lifestyle elements. people with Type 1 diabetes need lifelong insulin treatment to control their blood sugar levels.
– Autoimmune Nature:
The definite cause of Type 1 diabetes is not yet known, but it does involve a mixture of genetic and environmental factors that provoke an autoimmune response. This reaction destroys beta cells in the pancreas, the main reason for producing insulin.
– Dietary Considerations:
While insulin therapy is the main treatment for Type 1 diabetes, diet also plays an important part. A balanced diet may include a diabetes diet list with low glycemic index (GI) foods that can help manage blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of further problems.
How Is Blood Sugar Related to Diabetes?
The direct energy source for the body cells can be called blood sugar or glucose. Nevertheless, in people with diabetes, blood sugar levels can become dangerously high.
– Blood Sugar Levels and Their Significance:
Normal blood sugar levels typically range between 70 and 99 mg/dL when fasting, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. In people with diabetes, these levels are raised due to the body’s incompetence to use or produce insulin properly.
– The Impact of Diet on Blood Sugar Control:
Diet plays an important role in managing blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates notably impact blood sugar, breaking down into glucose during digestion. A diabetic diet focuses on controlling carbohydrate intake and choosing foods that have a low impact on blood sugar levels, like whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins.
What Is the Role of Insulin in Diabetes?
The pancreas produces insulin hormone that authorizes glucose to enter cells and be a primary energy source.
– Insulin Function in the Body:
When you eat, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which enters the bloodstream. Insulin authorizes cells to immerse in glucose and utilize it as energy. In people with diabetes, this process is disturbed, leading to high blood sugar levels.
– Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes:
In Type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to insulin, meaning that cells no longer respond to insulin as effectively. This leads to higher blood sugar levels and, with time, can cause the pancreas to produce less insulin.
– Insulin Therapy in Type 1 Diabetes:
People with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy because their bodies do not produce any insulin. Insulin can be regulated through injections or an insulin pump, which is important for maintaining blood sugar levels within a healthy range.
Is Glucose a Better Sugar Substitute in Diabetes?
In a diet with diabetes that concerns sweeteners, people often wonder if glucose is a better option than other sugars.
– The Role of Glucose and Other Sweeteners in Diet with Diabetes:
Glucose, fructose, and sucrose are all sugars that can raise blood sugar levels. However, glucose has a higher glycemic index (GI) than fructose, which increases blood sugar more quickly. For this reason, glucose is not a better sugar substitute for people with diabetes.
– Safe Alternatives for Diet with Diabetes:
Several sweeteners, such as stevia, erythritol, and monk fruit, are safer for people with diabetes. These sweeteners have little to no impact on blood sugar levels and can be used to satisfy sweet cravings without the risk of blood sugar spikes.
You can find more information about healthy diet at “Benefits of Healthy Eating”
What Is Pre-Diabetes Syndrome?
Pre-diabetes is a condition when blood sugar levels are more heightened than usual but not yet high enough to be categorized as diabetes.
– Definition and Importance of Early Detection:
Pre-diabetes is a warning sign that you are at risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. Early detection and lifestyle changes can prevent the progression to full-blown diabetes. A diet with diabetes plan that includes low-carbohydrate, high-fiber foods and regular physical activity can help normalize blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes.
Promising Ways to Manage Diet With Diabetes
Managing diabetes effectively requires a well-structured diet focusing on controlling blood sugar levels and preventing complications.
– Creating a Diet with diabetes Food List:
A diet with diabetes food list should include a variety of nutrient-dense foods low in carbohydrates and sugars. These foods include non-starchy vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats. Examples of foods include leafy greens, berries, nuts, seeds, and fish.
– Key Components of a Type 2 Diabetes Diet Plan:
A type 2 diabetes diet plan should focus on balancing carbohydrate intake with physical activity and medication (if needed). Portion control, meal timing, and choosing low-GI foods are also important for maintaining stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
– Foods to Avoid in a Diabetic Diet:
Certain foods can cause blood sugar spikes and should be limited or avoided in a diabetic diet. These diet with diabetes list should not include sugary drinks, processed snacks, white bread, and pastries. Instead, focus on whole, unprocessed foods that provide sustained energy and nutrients.
– Importance of Consistency and Monitoring:
Consistency is key in managing diabetes through diet. Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels and adjusting your diet can help you stay on track. Working with a healthcare provider or a dietitian can provide valuable guidance and support.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing diabetes through diet is one of the most effective ways to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications. By understanding the causes and symptoms of diabetes, recognizing the role of insulin and blood sugar, and making informed dietary choices, you can take control of your health and live a full, active life with diabetes.
Whether you have Type 1 or type 2, or are at risk of developing diabetes, adopting a diet with diabetes food list and avoiding foods that can cause blood sugar spikes are key steps toward better health.


6 thoughts on “10 PROMISING WAYS TO MANAGE DIET WITH DIABETES”